As you progress through this and the subsequent data courses, we will leverage all the benefits of Jupyter Notebook. You will have direct access to the Notebooks for each section. But, before you access the first Notebook, here’s a brief explanation of how they work:
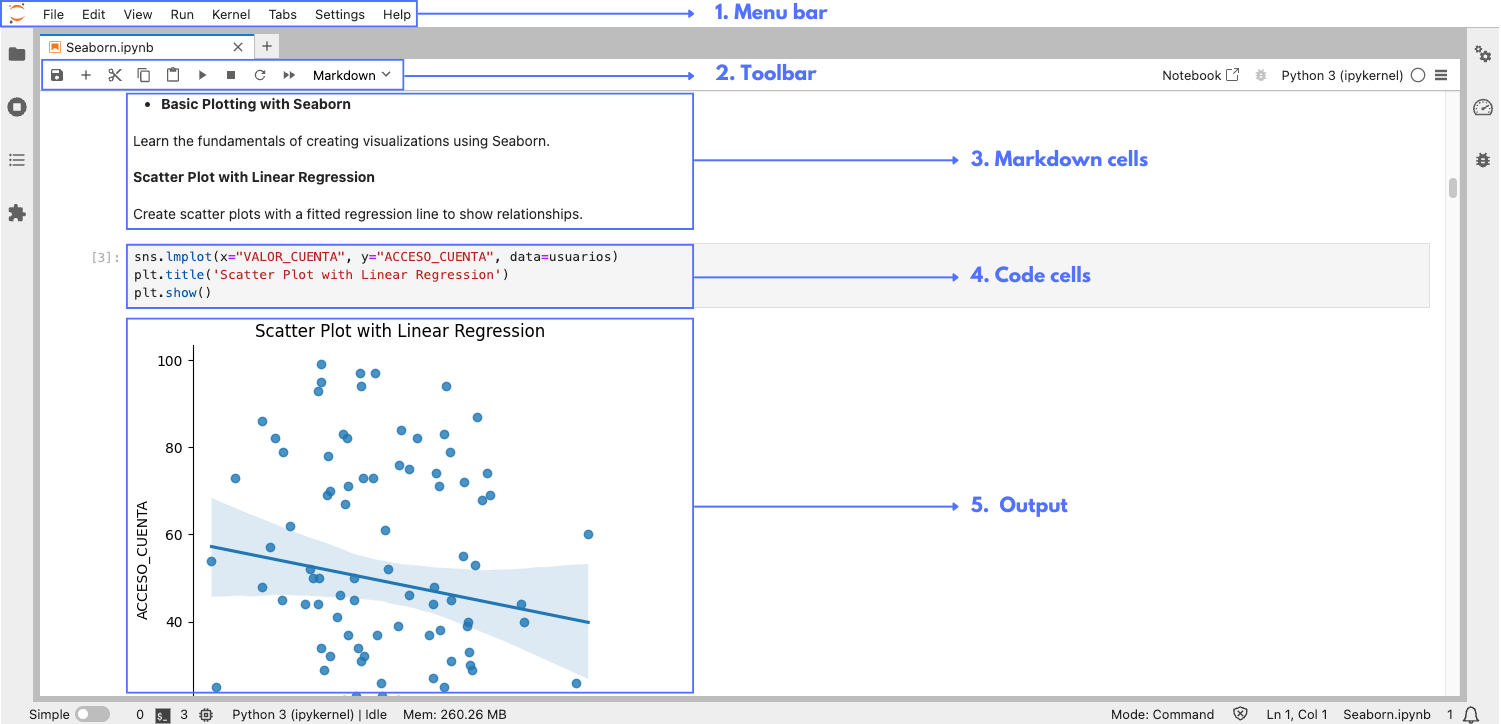
- Menu bar: The menu bar at the top of the interface provides access to various operations:
• File operations: Create new notebooks, open existing ones, save your work, and more.
• Edit options: Cut, copy, paste cells, and undo changes.
• View settings: Toggle the visibility of elements like the toolbar and header.
• Run menu: Run, stop, insert, change the type of cells.
• Kernel menu: Manage the notebook’s computational engine, including restarting it. The computational engine is the part that run the code that you are writing in the notebook.
• Tab menu: Manage the tabs of your different notebooks.
• Settings menu: Access to the configuration of the different general options of the environment: language, autosave, font size...
• Help menu: Access documentation and support resources.
- Toolbar: The toolbar provides quick access to common actions:
• Save: Save your notebook (Ctrl + S or Cmd + S on Mac).
• Add cell: Add a new cell below the current one (+ button).
• Cut/Copy/Paste cells: Manage cells easily.
• Run cells: Execute the code in the selected cell (Shift + Enter)
• Interrupt the kernel: Stop the notebook’s computational engine.
• Restart the kernel: Restart the notebook’s computational engine.
• Restart the kernel and run the cells: Restart the notebook’s computational engine and run every cell of the notebook.
• Change the cell type: Change the type (Markdown or Code) of the selected cell.
- Markdown cells: Markdown cells are used to add formatted text, making it easy to include documentation, explanations, and links within your notebook. Markdown supports headings, lists, links, images, and more. Think of these cells as the places where you can write different things and present them.
• Writing markdown: Select a cell, change it to Markdown (using the toolbar or by pressing M), and write your formatted text.
• Rendering markdown: To render the Markdown text, press Shift + Enter.
- Code cells: Code cells are used to write and execute code. When you run a code cell, the output is displayed directly below the cell. This allows you to see the results of your code immediately.
• Running code: Click on the cell and press Shift + Enter, or click the Run button in the toolbar.
• Output: The results of the code execution appear below the code cell.
- Output: The output of a code cell is the result generated from the execution of the code. This output is displayed directly below the code cell and can include various types of results such as text, images, plots, or interactive elements. For example, executing a code cell containing a print statement will display the printed text below the cell, while executing a cell with a plot command will render the plot in the output area (as in the image).